Discover the essential role of macromolecules in our diet through this comprehensive guide, macromolecules in my food answer key. Delve into the fascinating world of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, exploring their structures, functions, and significance in maintaining optimal health.
Macromolecules are the building blocks of life, providing energy, structure, and genetic information. Understanding their diverse roles in our food choices empowers us to make informed decisions for a balanced and nutritious diet.
Macromolecules in Food: Macromolecules In My Food Answer Key
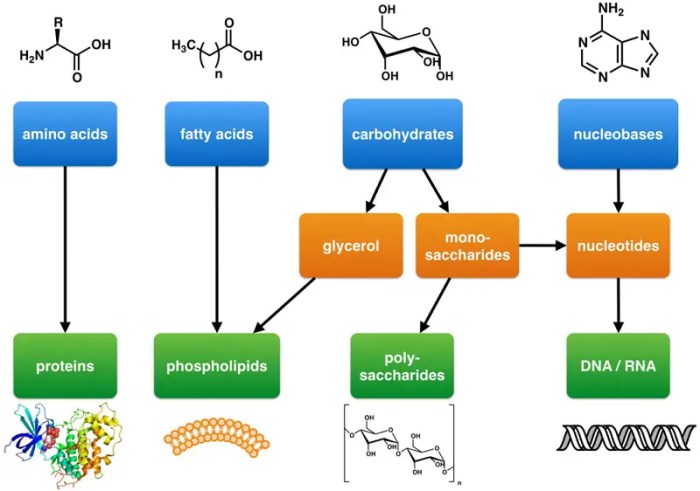
Macromolecules are large, complex molecules that are essential for life. They are found in all living things, including food. There are four main types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Macromolecules are important for food because they provide energy, build and repair tissues, and regulate body functions. Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. Proteins are used to build and repair tissues. Lipids are used to store energy and insulate the body.
Nucleic acids are used to store and transmit genetic information.
Types of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are classified into three types: sugars, starches, and fiber. Sugars are simple carbohydrates that are quickly digested and absorbed by the body. Starches are complex carbohydrates that are slowly digested and absorbed by the body.
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the body. It is important for digestive health.
Proteins
Proteins are made up of amino acids. They are essential for building and repairing tissues. Proteins also play a role in metabolism, hormone production, and immune function.
Lipids
Lipids are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. They are used to store energy and insulate the body. Lipids also play a role in hormone production and cell signaling.
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides. They are used to store and transmit genetic information. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA.
Functions of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide energy for the body. They are broken down into glucose, which is then used by cells for energy.
Proteins
Proteins are used to build and repair tissues. They also play a role in metabolism, hormone production, and immune function.
Lipids
Lipids are used to store energy and insulate the body. They also play a role in hormone production and cell signaling.
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are used to store and transmit genetic information. They are essential for cell division and reproduction.
Sources of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
| Food | Carbohydrates (g) |
|---|---|
| Bread | 25 |
| Rice | 28 |
| Pasta | 27 |
| Potatoes | 21 |
| Fruit | 15-20 |
Proteins
| Food | Protein (g) |
|---|---|
| Meat | 25-30 |
| Fish | 20-25 |
| Poultry | 20-25 |
| Eggs | 6 |
| Beans | 15 |
Lipids
| Food | Lipids (g) |
|---|---|
| Butter | 80 |
| Oil | 100 |
| Nuts | 15-20 |
| Seeds | 10-15 |
| Avocado | 15 |
Nucleic Acids
| Food | Nucleic Acids (mg) |
|---|---|
| Meat | 100-150 |
| Fish | 80-120 |
| Poultry | 80-120 |
| Eggs | 20 |
| Beans | 30 |
Recommended Daily Intake
Carbohydrates
The recommended daily intake of carbohydrates is 45-65% of total calories.
Proteins
The recommended daily intake of protein is 10-35% of total calories.
Lipids
The recommended daily intake of lipids is 20-35% of total calories.
Nucleic Acids
There is no recommended daily intake for nucleic acids. However, it is important to consume a diet that is rich in nucleic acids.
Dietary Considerations, Macromolecules in my food answer key
Importance of a Balanced Diet
It is important to eat a balanced diet that includes all four types of macromolecules. A balanced diet will provide the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly.
Impact of Excessive or Insufficient Macromolecule Intake
Excessive or insufficient intake of any type of macromolecule can have negative consequences for health. For example, excessive carbohydrate intake can lead to weight gain and obesity. Insufficient protein intake can lead to muscle loss and weakness. Insufficient lipid intake can lead to dry skin and hair.
Insufficient nucleic acid intake can lead to impaired cell growth and development.
Tips for Incorporating Macromolecules into a Healthy Diet
Here are some tips for incorporating macromolecules into a healthy diet:
- Choose whole grains over refined grains.
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Include lean protein sources in your diet.
- Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats.
- Choose healthy sources of nucleic acids, such as meat, fish, and beans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary types of macromolecules?
The four main types of macromolecules are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Why are carbohydrates important in our diet?
Carbohydrates provide the body with energy and are essential for brain function.
What is the role of proteins in the body?
Proteins are involved in a wide range of functions, including building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes, and transporting molecules.
What are the health benefits of consuming lipids?
Lipids provide energy, support cell growth, and help the body absorb vitamins.
How do nucleic acids contribute to our genetic makeup?
Nucleic acids, specifically DNA and RNA, carry genetic information and are responsible for protein synthesis.