An activity-based costing system that is designed for internal decision-making sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This innovative approach to cost accounting provides organizations with unparalleled visibility into their operations, enabling them to make informed decisions that drive profitability and success.
As we delve into the intricacies of activity-based costing, we will explore its fundamental concepts, unravel its components, and witness its transformative impact on organizational decision-making. Through a comprehensive case study, we will gain firsthand insights into the implementation process, challenges encountered, and the remarkable outcomes achieved.
Join us on this captivating journey as we unlock the power of activity-based costing and empower organizations to reach new heights of efficiency and profitability.
1. Definition and Purpose
An activity-based costing (ABC) system is a costing method that assigns costs to activities based on the resources consumed by those activities. The primary purpose of an ABC system is to provide more accurate and detailed information about the costs of products or services, which can be used to improve decision-making.
ABC systems are based on the assumption that activities consume resources, and that the costs of those resources can be assigned to products or services based on the amount of activity that is required to produce them. This is in contrast to traditional costing methods, which assign costs to products or services based on factors such as direct labor hours or machine hours.
Limitations and Assumptions of ABC Systems, An activity-based costing system that is designed for internal decision-making
- ABC systems can be complex and time-consuming to implement.
- ABC systems require a large amount of data to be collected and analyzed.
- ABC systems are based on the assumption that activities consume resources, and that the costs of those resources can be assigned to products or services based on the amount of activity that is required to produce them. This assumption may not always be valid.
2. Components of an ABC System
The key components of an ABC system include:
- Activities: Activities are the tasks or processes that are performed in an organization. Activities can be classified as either value-added or non-value-added.
- Cost drivers: Cost drivers are the factors that cause costs to be incurred. Cost drivers can be classified as either activity-level cost drivers or facility-level cost drivers.
- Cost pools: Cost pools are groups of costs that are assigned to activities based on the cost drivers.
Identifying and Classifying Activities and Cost Drivers
The first step in implementing an ABC system is to identify and classify the activities and cost drivers in the organization. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as time studies, interviews, and process mapping.
Role of Cost Pools in Allocating Costs to Activities
Cost pools are used to allocate costs to activities based on the cost drivers. The cost driver for a particular cost pool is the factor that causes the costs in that cost pool to be incurred.
3. Activity Analysis and Cost Allocation
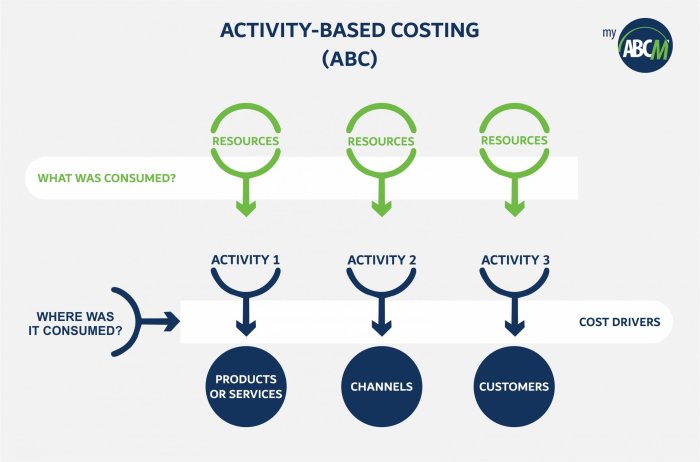
Activity analysis is the process of studying activities to determine their costs and their relationship to products or services. Activity analysis can be used to identify opportunities to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Cost allocation is the process of assigning costs from cost pools to activities. Cost allocation can be done using a variety of methods, such as the direct method, the indirect method, and the activity-based method.
Common Cost Drivers and Their Applications
Some common cost drivers and their applications include:
- Number of transactions: This cost driver is used to allocate costs that are related to the number of transactions that are processed.
- Machine hours: This cost driver is used to allocate costs that are related to the use of machinery.
- Labor hours: This cost driver is used to allocate costs that are related to the use of labor.
4. Benefits and Challenges of ABC Systems: An Activity-based Costing System That Is Designed For Internal Decision-making

ABC systems can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Improved cost visibility
- Improved decision-making
- Reduced costs
However, ABC systems also have some challenges, including:
- Complexity
- Data collection
- Cost
Comparison of ABC Systems to Traditional Costing Methods
ABC systems differ from traditional costing methods in a number of ways. Traditional costing methods assign costs to products or services based on factors such as direct labor hours or machine hours. ABC systems, on the other hand, assign costs to products or services based on the activities that are required to produce them.
ABC systems are more accurate and detailed than traditional costing methods. However, ABC systems are also more complex and time-consuming to implement.
5. Case Study
Implementing an ABC System
The following is a case study of an organization that successfully implemented an ABC system:
Company: XYZ Corporation
Industry: Manufacturing
Challenge: XYZ Corporation was facing increasing competition and needed to find ways to reduce costs.
Solution: XYZ Corporation implemented an ABC system to identify and reduce costs.
Results: XYZ Corporation was able to reduce costs by 10% by implementing an ABC system.
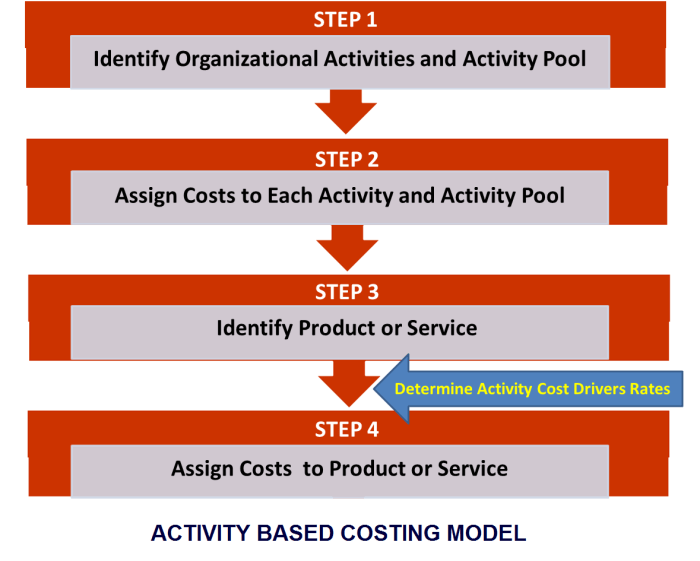
Key Steps Involved in Implementing an ABC System
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify and classify activities |
| 2 | Identify and classify cost drivers |
| 3 | Create cost pools |
| 4 | Allocate costs to cost pools |
| 5 | Allocate costs from cost pools to activities |
| 6 | Use ABC information to make decisions |
FAQ Resource
What are the key benefits of implementing an activity-based costing system?
An activity-based costing system offers numerous benefits, including improved cost visibility, enhanced decision-making, accurate product costing, and optimized resource allocation.
What are the challenges associated with implementing an activity-based costing system?
Implementing an activity-based costing system can be challenging due to data collection requirements, complexity, and the need for organizational commitment.
How does activity-based costing differ from traditional costing methods?
Activity-based costing focuses on activities as the cost drivers, while traditional costing methods rely on volume-based measures such as direct labor hours or machine hours.
What is the role of cost drivers in an activity-based costing system?
Cost drivers are factors that cause costs to vary and are used to allocate costs from cost pools to activities.
How can organizations ensure the accuracy of their activity-based costing system?
Organizations can ensure accuracy by carefully identifying and classifying activities, selecting appropriate cost drivers, and regularly reviewing and updating the system.