Forensic science processes securing and packaging evidence – Forensic science processes for securing and packaging evidence play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and authenticity of evidence, ensuring its admissibility in court and its ability to provide crucial insights in criminal investigations.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential procedures for evidence handling, the significance of the chain of custody, and the selection of appropriate packaging materials. It also explores the challenges and considerations associated with securing biological and digital evidence, and emphasizes the ethical and legal implications of forensic evidence handling.
Evidence Securing and Packaging: Essential Procedures: Forensic Science Processes Securing And Packaging Evidence

Evidence securing and packaging are critical steps in forensic science to ensure the integrity and authenticity of evidence. The primary objective is to prevent contamination, alteration, or loss of evidence, preserving its evidentiary value throughout the investigation and legal proceedings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Evidence Handling Techniques, Forensic science processes securing and packaging evidence
- Wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and masks, to prevent contamination.
- Document the condition and location of the evidence before handling.
- Minimize handling and move evidence only when necessary.
- Package evidence in clean, sealed containers that are appropriate for the type of evidence.
- Label evidence with unique identifiers, including case number, date, time, and location.
- Maintain a secure chain of custody to track the movement of evidence.
Chain of Custody: Ensuring Evidence Traceability
The chain of custody is a chronological documentation of the transfer of evidence between individuals and locations. It establishes a clear record of who handled the evidence, when, and for what purpose. This documentation ensures that the evidence has not been tampered with or compromised, preserving its integrity and admissibility in court.
Best practices for maintaining a secure chain of custody include:
- Documenting all transfers of evidence with signatures and timestamps.
- Limiting access to evidence to authorized personnel only.
- Storing evidence in a secure location with controlled access.
- Using tamper-evident seals or containers to prevent unauthorized access.
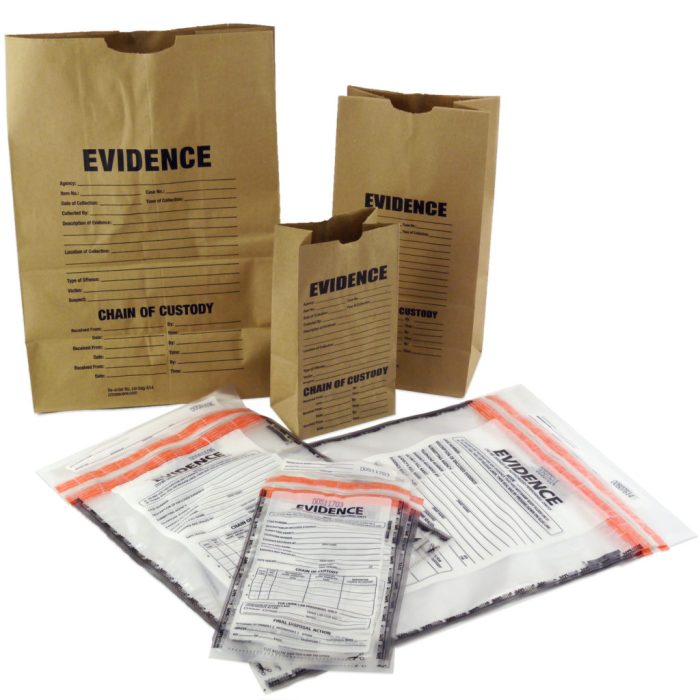
Evidence Packaging Materials: Selecting the Right Tools
The selection of appropriate evidence packaging materials is crucial to preserve the integrity of evidence. Common materials include:
- Paper envelopes: Suitable for documents, photographs, and small items.
- Plastic bags: For non-porous items, such as clothing or weapons.
- Glass or metal containers: For liquid or biological evidence.
- Vacuum-sealed bags: For evidence that requires protection from air or moisture.
- Evidence collection kits: Pre-packaged kits containing specific materials for specific types of evidence.
Evidence Labeling and Documentation: Ensuring Clarity and Accountability

Proper labeling and documentation of evidence are essential for tracking and maintaining its integrity. Evidence should be labeled with the following information:
- Case number and item number
- Date and time of collection
- Location of collection
- Description of evidence
- Collector’s signature
Documentation should also include photographs, sketches, or notes of the evidence’s condition and location.
Transportation and Storage of Evidence: Maintaining Integrity
Evidence transportation and storage must be handled with care to preserve its integrity. Factors to consider include:
- Temperature and humidity control to prevent deterioration or contamination.
- Secure packaging to prevent damage or loss.
- Transportation in a secure vehicle with limited access.
- Storage in a secure location with controlled access and environmental monitoring.
Q&A
What is the primary objective of evidence securing and packaging?
To preserve the integrity and authenticity of evidence, ensuring its admissibility in court and its ability to provide accurate information in criminal investigations.
Why is maintaining the chain of custody crucial in forensic science?
The chain of custody documents the transfer of evidence between individuals and locations, ensuring its traceability and preventing tampering or contamination.
How should evidence be labeled and documented?
Evidence should be labeled with unique identifiers, including case number, item description, date, and collector’s initials. Documentation should include a detailed description of the evidence, its condition, and any observations made during collection.
What are the unique challenges associated with securing and packaging biological evidence?
Biological evidence, such as DNA or bodily fluids, requires specialized handling techniques to prevent contamination and preserve its integrity. Proper storage and transportation methods are crucial to maintain the viability of biological evidence for analysis.
What ethical and legal responsibilities do forensic scientists have in handling evidence?
Forensic scientists have a duty to handle evidence ethically and legally, adhering to established protocols and standards to ensure its admissibility in court. They must avoid contamination, bias, and any actions that could compromise the integrity of the evidence.