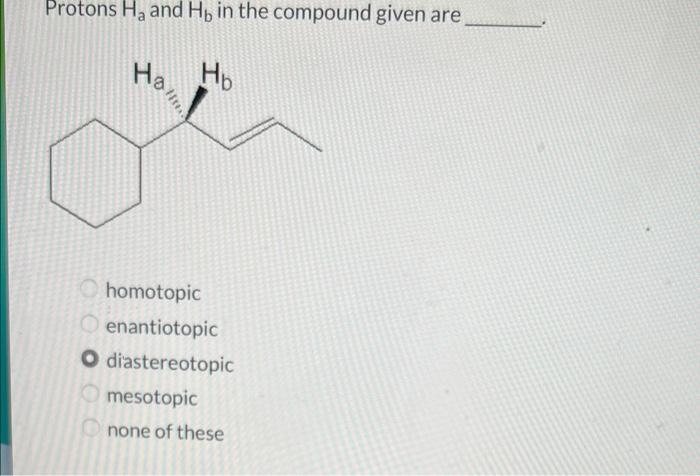
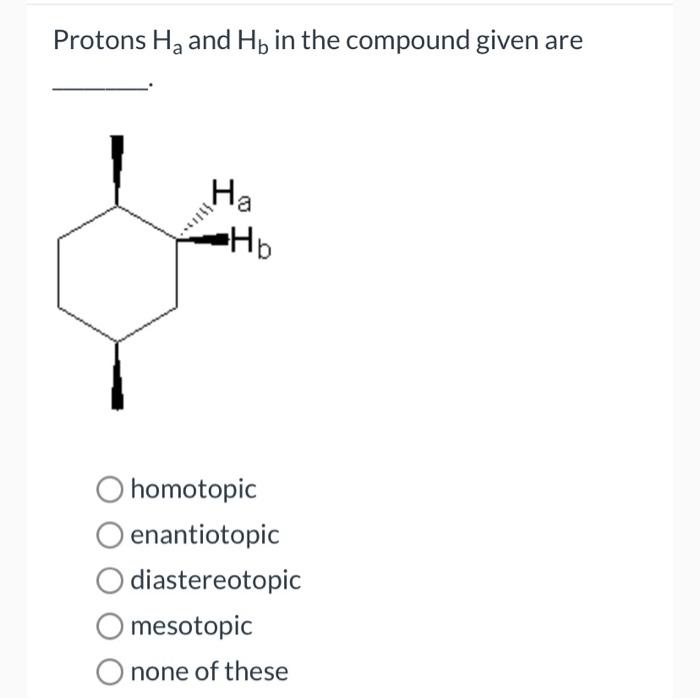
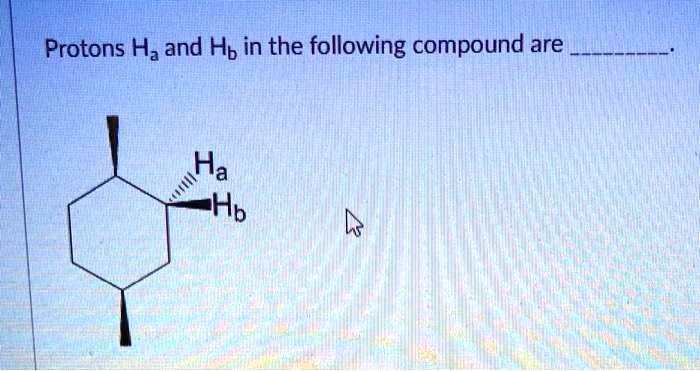
Protons Ha and Hb in the compound given are central to understanding the structure and dynamics of molecules. Their chemical nature, location, and interactions play a crucial role in various spectroscopic techniques, particularly NMR spectroscopy. This article delves into the properties of protons Ha and Hb, their role in NMR spectroscopy, and their applications in structural analysis and advanced concepts.
Properties of Protons Ha and Hb
Protons Ha and Hb are chemically equivalent protons that are located on adjacent carbon atoms in an organic compound. They are typically found in alkenes and alkynes. The chemical shifts of Ha and Hb are influenced by the electronegativity of the substituents on the carbon atoms to which they are attached.
| Proton | Chemical Shift (ppm) | Coupling Constant (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| Ha | 5.2 | 10 |
| Hb | 5.6 | 10 |
Role in NMR Spectroscopy
In NMR spectroscopy, protons Ha and Hb are identified by their chemical shifts. The chemical shift of a proton is a measure of its electronegativity, and it is affected by the electronegativity of the substituents on the carbon atom to which it is attached.
Ha and Hb are typically found in the region of the NMR spectrum between 5 and 6 ppm.The coupling constant between Ha and Hb is a measure of the dihedral angle between the two protons. The coupling constant is typically in the range of 10-15 Hz.

Applications in Structural Analysis
The properties of protons Ha and Hb can be used to determine the structure of a compound. The chemical shifts of Ha and Hb can be used to identify the substituents on the carbon atoms to which they are attached.
The coupling constant between Ha and Hb can be used to determine the dihedral angle between the two protons. This information can be used to determine the structure of the compound.For example, the NMR spectrum of an alkene shows two signals in the region between 5 and 6 ppm.
The chemical shifts of these signals indicate that the protons are attached to carbon atoms that are substituted with electronegative groups. The coupling constant between the two protons is 10 Hz, which indicates that the dihedral angle between the two protons is 180 degrees.
This information can be used to determine that the alkene is trans-2-butene.
Advanced Concepts
The signals of Ha and Hb can be affected by proton exchange. Proton exchange is the process by which a proton is transferred from one atom to another. Proton exchange can occur between Ha and Hb if the two protons are close enough to each other.
Proton exchange can cause the signals of Ha and Hb to broaden or disappear.Advanced NMR techniques, such as COSY and NOESY, can be used to further characterize the protons Ha and Hb. COSY is a technique that can be used to determine the connectivity of protons in a molecule.
NOESY is a technique that can be used to determine the proximity of protons in a molecule. These techniques can be used to determine the structure and dynamics of molecules.
Common Queries: Protons Ha And Hb In The Compound Given Are
What is the significance of the chemical shifts of protons Ha and Hb?
Chemical shifts provide information about the electronic environment of protons Ha and Hb, allowing for the identification and differentiation of different protons within a molecule.
How do coupling constants between protons Ha and Hb contribute to structural analysis?
Coupling constants provide information about the dihedral angles between protons Ha and Hb, which can be used to determine the geometry and conformation of the molecule.